Android is an open source mobile operating system developed by Google, which is based on Linux. There are many features available in this like mobile games, cameras etc. Due to this, Android has become the most used operating system in the present time. Android was developed by Android Inc., a company that was acquired by Google in 2005. The company was later placed by Google in the Open Handset Alliance (OHA). In April 2013, more than 1.5 million Android phones were activated every day. In total, more than 900 million Android devices were activated in May 2013.
Linux is an operating system like Unix. This is the most successful and most popular software of open source software. It is available for general use under the GPL v2 license and part of it is inspired by Unix.
3. Ubuntu

Ubuntu is a Linux operating system. It first came in October of 2004. It is based on Debian Linux and today there are many other Linux Dictribution based on this such as Linux Mint.
Google Chrome OS is an operating system based on the Linux kernel and uses Google Chrome as the main user interface. As a result, ChromeOS supports Google's web application. It was announced on July 7, 2009, which describes it as an operating system, which stores both users and application data in their cloud server. Chrome OS has a media player and an integrated file manager. It supports the Chrome app, which looks like remote access to the original applications as well as the desktop. Some Android apps are available for operating systems from 2014. Chrome OS Open Source Project is based on Chromium OS, which can be compiled from download source code unlike Chrome OS.
FreeBSD is a free UNIX operating system. The goal of the FreeBSD project is to provide a system that can be used for anything with the least possible restrictions.
iOS is a mobile operating system of the multinational Apple Inc. Originally developed for the iPhone (iPhone OS), then it has been used on devices such as iPod touch and iPad. It does not allow the installation of iOS on third-party hardware. The control elements consist of sliders, switches and buttons. The response to the user's orders is immediate and provides a fluid interface. The interaction with the operating system includes gestures such as slips, touches, pinches, which have different definitions depending on the context of the interface. Internal accelerometers are used to make some applications respond to shake the device (for example, for the undo command) or rotate it in three dimensions (a common result is to change from landscape to landscape or landscape).
Fedora is an RPM based Linux distribution. The Fedora project was born from the Warren Togami initiative which needed to create high quality RPM Package Manager packages for Red Hat Linux. On September 25, 2003, the first release of Fedora Core was born, the FC 0.94, also known as Fedora Core 1 test 2 and with the code name Severn. The Fedora project was born from the Warren Togami initiative which needed to create high quality RPM Package Manager packages for Red Hat Linux. Fedora is an RPM based Linux distribution. The goal of the developers of the distribution is to promote Free Software and to design an operating system for as diverse a target group as possible. The development is being organized in the online community of the Fedora project, led by Red Hat. Fedora is the direct successor to Red Hat Linux. The Red Hat company provides jobs to many developers of Fedora, but the company does not provide any business support or services for the distribution.
mac OS formerly known as Mac OS X and after then OS X, this operating system is a series of graphical operating systems developed and marketed by Apple Inc. since 2001. It is the main operating system for Apples Mac computer family. Within the market of desktop, laptop and home computers, and through the use of the web, it is the second most used desktop operating system, after Microsoft Windows.
Chromium OS is a Linux distribution unlike Google Chrome OS. The source code is freely available and usable. Chromium OS contains the substring instead of Google Chrome BSD license standing Chromium browser. New Chrome OS version is derived from the current Chromium OS development and are complemented by several commercial programs such as Google Chrome, Adobe Flash, PDF plugin, Netflix and Google Hangouts. Chromium OS was built on the basis of a Linux kernel, in an Ubuntu 10.04 environment, using the official package manager of the Gentoo Linux distribution, Portage.
Red Hat Linux was an operating system based on Linux from the production company Red Hat. Intended for home users, production was stopped in 2004 and stayed release Red Hat Enterprise Linux. Since 2003, Red Hat has shifted its focus to the business market with the Red Hat Enterprise Linux distribution and the non-commercial Fedora Core version. Red Hat Linux 9 the final version, officially arrived at the end of its useful life on April 30, 2004. Although the Fedora Legacy project continued publishing updates, until the project was abandoned at the end of 2006.
OpenBSD is a Unix like free and open source operating system derived from AT&T UNIX through the Berkeley Software Distribution (BSD) branch, a research Unix derivative developed at the University of California, Berkeley. At the end of 1995, Theo de Raadt branched out from NetBSD. In addition to the operating system as a whole, the project saves a portable version of many subsystems, especially OpenSSH, which is available as a package on other operating systems. This project is known for its developers' insistence on open source code, good documentation, code correctness, and security. This project has a strict policy on licensing, preferring the ISC license and other variations of the simplified BSD license. Many of the security features are optional or not in other system operations. Developers often audit source code for software bugs and security holes. De Raadt coordinated this project from his home in Calgary, Alberta, Canada. The logo and mascot are puffer fish named Puffy.
Haiku is an open source operating system currently under development that focuses specifically on personal and multimedia computing. Inspired by BeOS (Be Operating System), Haiku aims to become a fast, efficient, easy to use and easy to learn system, without neglecting its power for users of all levels. The project is led by Haiku Inc., a nonprofit organization located in New York. Haiku has its own modular micro nucleus called NewOS, which will be highly optimized for work with audio, video, graphics, and animations in three dimensions inspired by the original BeOS. Its architecture provides advanced core accommodates multiple processors, high performance, bandwidth input/output and a penetrating modular system multi threaded for system re-entrant processes multitasking, graphical flexibility and response Real time, unlike other operating systems Haiku OS is natively graphic, inherited from BeOs, Visual programming by nodes from the outputs of the programs that allow it through a native software called Cortex.
13. Debian

SunOS was the version of the operating system derived from UNIX and BSD developed by Sun Microsystems for its workstations and servers until the beginning of the 1990s. This was based on the UNIX BSD with some additions of the System V UNIX in later versions. SunOS is a version of UNIX used in Sun Microsystems workstations which was released in 1982. After releasing SunOS version 4, Sun Microsystems changed the UNIX BSD code they had previously used with the UNIX System V code, after obtaining a license from the UNIX licensee at that time, AT&T. This change made the name change to Solaris version 2, from what SunOS should have been 5. So, indirectly, SunOS was considered as Solaris version 1.x.
System 7 is a version of Mac OS, the operating system of Macintosh personal computers introduced on May 13, 1991, and was the main operating system of the Mac until it was replaced by Mac OS 8 in 1997. Features added to System 7 included Cooperative Multitasking, virtual memory, personal file sharing, QuickTime, QuickDraw 3D and an improved graphical interface. Nowadays it is still used by a small number of Macintosh users that use computers based on Motorola 68000 family microprocessors. Note that "System 7" is used as a generic term to refer to all its versions. With the release of version 7.6 in 1997, Apple officially changed the name of the operating system to Mac OS, a name that first appeared in System 7.5.1. System 7 was developed for Motorola 68k processors but was ported to PowerPC, when Apple adopted the use of the new processor.
Ubuntu Privacy Remix (UPR) is a modified live CD based on the Ubuntu Linux distribution. UPR is not intended for permanent installation on the hard disk. UPR developers believe that the threat of theft of sensitive data today is no longer limited to ordinary cyber criminals and their Trojan horses, rootkits and keyloggers. Rather, in many countries of the world, the government is taking measures to spy on and monitor citizens' computers by such means. Ubuntu Privacy Remix is designed as a tool to protect your data against unauthorized access.
17. MenuetOS

MenuetOS, also known as MeOS, is a free operating system created by Ville Mikael Turjanmaa for PC x86, written entirely in assembly language (FASM) for 32 and 64 bits. It reached version 1.0 on May 15, 2015 for the 64 bit version, considered by its creator as the first official release of the operating system. Its core is real-time, monolithic, with preferred multitasking, which includes video controllers, networks, audio, USB devices, keyboards, TV tuners, webcams and printers, among other types of devices. Its development has focused on the objective of allowing it to develop efficiently, simply and quickly. It has a graphic desktop, games and connectivity, using a TCP/IP stack. Even so, it fits on a flexible disk of 1.44 MB. It also facilitates easy and complete programming in assembly language. This is contrary to the usual view according to which assembly language is only useful in old or embedded systems.
18. Mac OS 8

Mac OS 8 is an operating system developed and marketed by Apple Computer on 26 of July, 1997. It is the biggest overhaul of Mac OS since the release of System 7.
19. ReactOS

20. Zorin OS

21. JavaOS

JavaOS is an operating system, discontinued since 2006. It was developed by Sun Microsystems and unlike Windows, Mac OS and Unix which are written in the C language, JavaOS is written in Java.
Windows 10 is an operating system for personal computers developed and released by Microsoft as part of the operating system family Windows NT. It was released on July 29, 2015. It is the first version of Windows for which feature updates are constantly being released. Devices in enterprise environments can receive these updates at a slower pace or only receive critical updates, such as security patches, during the ten-year lifetime of extended support. The development of Windows Threshold started shortly after the completion of Windows 8 and simultaneously with the development of Windows 8.1. The update would take a step back from the Windows 8 vision by making the start screen optional. During Build 2014, Microsoft announced some features of "the next iteration of Windows", including the return of the start menu and the ability to run Modern UI apps within the desktop.
MaRTE OS (Minimal Real-Time Operating System for Embedded Applications) is a real-time operating system that implements the services defined in the POSIX.13 standard. MarteOS is a real-time operating system for embedded applications that follows the minimum real-time POSIX .13. The project is developed by the Computer and Real Time Group at the University of Cantabria, although there are also collaborators in different places. It allows to run embedded applications written in Ada and C. This operating system works either directly on PC or emulator. The development environment is based on the GNU compilers GNAT, GCC and GCJ.
24. Xubuntu

Qimo 4 Kids was a kid-friendly environment, built entirely with free software. Qimo comes pre-installed with educational games for children. The interface has large colorful icons that makes it easy for users to navigate easily. It is designed especially for children of school. It's a pretty simple idea, it's a customized version of Xubuntu, designed to be visually appealing, yet not overwhelming to children. Qimo is based on Xubuntu, maintained by the community derived from the Ubuntu operating system, using the Xfce desktop environment. This helps to provide low hardware requirements, minimum of 256 MB of memory to run from the CD, or 192 MB to install. At least 6 GB of hard disk space is recommended, and a CPU of 400 MHz or higher. Qimo 2.0 was launched in May 2010 and stopped developing in 2012.
The Möbius operating system is an open source operating system for the IA-32 platform (Intel i386 and compatible). The authors focused the development on some very important points for a modern operating system. The main objectives of Möbius are: (1). Make it sufficiently extensible to make the development of new device drivers and technologies easier. (2). Keep the kernel as small and modular as possible. (3). Support existing applications whenever possible. (4). Stay easy to use enough to have a Mobius system installed and configured without having to learn anything.
27. Oracle Linux

Symbian OS is an operating system designed for mobile devices and smartphones, with reference to related libraries, user interfaces, frameworks and common tools that were originally developed by Symbian Limited. It is descended from Psion's EPOC and runs exclusively on ARM processors only. Nokia acquired Symbian Software Limited in 2008 and established a new independent nonprofit organization named Symbian Foundation. Symbian OS and related user interfaces, S60, UIQ and MOAP(S) were donated to the organization by its owners for the purpose of making Symbian platform a royalty free, open source software. This platform was named as the successor to the Symbian OS after the official inauguration of the Symbian Foundation in April 2009. In February 2010, the Symbian platform was officially made available as open source code. It contributed 46.9% on the sale of Symbian-based equipment and smartphones, due to this it became the world's most popular mobile operating system.
Windows NT (Windows New Technology) is a member of Microsoft's operating system, whose first version was published in July 1993. Windows NT Technology is a 32-bit Microsoft operating system designed to work in a large network environment. Windows versions released after 2000 are actually Windows NT but do not officially use this name. Prior to the presence of Windows 95, Microsoft Company conceived and shaped a new line of operating systems oriented for workstation and network servers. In the first instance it was primarily intended for professional use, only with Windows XP is the 'professional' line also intended for home use.
NTDIOS Networ Disk OS is a working 32-bit, multitasking, OS for x86-based computers, running in protected mode.
31. Red Hat Enterprise Linux

32. Symobi

The basis of Symobi is the message-oriented operating system µnOS, which is on its part based on the real-time microkernel Sphere.
33. Amiga OS

Windows Server 2003 R2 is an improved version of Windows Server 2003 that was released in December 2005, but older users are not free to update to the new version, but require a paid update. However, R2 is currently on the market. In addition to Win2K3 SP1, the content of R2 has another CD, which contains more new features. It is based on NT technology and the version of the NT kernel is 5.2. In general terms, Windows Server 2003 could be considered as a modified Windows XP for business tasks, not with fewer functions, but these are disabled by default to obtain better performance and to center the use of processor in the server characteristics, for example, the graphical interface called Luna in Windows XP is disabled, so only the classic Windows interface is used.
MS-DOS (acronym - Microsoft Disk Operating System) was an operating system from Microsoft, now no longer in production. Its dedicated to the personal computer with a microprocessor x86. MS-DOS Marketed from 1982 to 2000, it was the first in a long series of Microsoft operating systems that in the 1980s accounted for over 90% of the global operating system market and, until the advent of Windows 95 in 1995, was the operating system for the most widespread computer in the world. MS-DOS was born in 1980. When tasked with Microsoft to produce an operating system for personal computers range of IBM PC of IBM. At this time, Microsoft bought the rights to QDOS, also known as 86-DOS, of Seattle Computer Products that was developed by Tim Paterson, and began working on the modifications to meet IBM's requirements.
Chinese operating system referred to as: COS is a operating system by the Institute of Software, Chinese Academy of Sciences and Shanghai Alliance Tong Network Communications Technology Co., Ltd. This is a jointly designed and developed operating system, released on January 15, 2014 in Beijing's Diaoyutai State Guesthouse. It claims that the system already has 100,000 applications. It claims that the system already has 100,000 applications. The system uses the Linux kernel to provide a user-level hardware abstraction layer, data layer and media layer, and supports multiple runtime environments. According to reports, the operating system has China's completely independent intellectual property rights, the Chinese Academy of Sciences is intended to break the monopoly of the US series of manufacturers.
37. Sabayon

38. Windows 98 SE

On June 25, 1998 Microsoft launched Windows 98, which was a better version of Windows 95. It included new hardware drivers and the FAT32 file system that supported partitions larger than the 2GB allowed by Windows 95. This edition is one of the latest for PC-9821. In 1999 Microsoft released Windows 98 second edition, whose most notable feature was the ability to share between several computers an Internet connection through a single telephone line and some improvements to the original Windows 98.
USIX is a Unix-like operating system created by System Six Inc. and INEUM. USIX, complied with the main international standards and agreements (POSIX 1003.1b-1993, SVID), supported real-time mode, had built-in protection against unauthorized access (security level C2), etc. Binary compatible with SVR4 / 386. After System Six closed, OS development ended.
40. Redox

Windows 7 is an operating system of the Microsoft Windows family. This computer software is the new operating system released by Microsoft Company on October 23, 2009. Microsoft has made several improvements to make it more user-friendly than its previous operating system 'Vista'. Microsoft says it's the simplest and best operating system in its history. Some features are:- 1. Finding this can be done at a fast pace. 2. Browsing is easier than ever. 3. Better networks - Wi-Fi, mobile broadband corporate VPN etc. can be opened with the help of just one click. 4. Device-friendly - With this help camera, printer etc. can be easily added. 5. Less driver requirement - Most drivers are installed in Windows 7.
42. Nova

43. Cromix
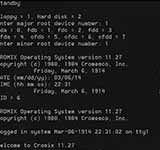
Cromemco released CROMIX, the first Unix-like OS for microcomputers. CROMIX run on Cromemco systems using the Motorola 68000 series of microprocessors.
Xenix is a UNIX descendant operating system that was purchased by Microsoft Corporation from AT&T as a developer of UNIX Version 7 in 1979. This operating system was introduced on August 25, 1980, and became the most popular UNIX operating system of its time.
Windows 8 is an operating system developed by Microsoft for use on computers, laptops and tablets and is the successor to Windows 7. The RTM version was released on August 1, 2012 and the final consumer version has been available since October 26, 2012. TechNet and MSDN users (or another type of account with the option to obtain a license from Windows 8) were able to use the operating system from August 15, 2012. Windows Server 2012 was released at about the same time as Windows 8. Windows 8 was succeeded by Windows 8.1 on October 17, 2013. Windows 8.1 is available for free in the Windows Store for anyone with Windows 8.
LynxOS is a unixoides real-time operating system of the Californian company Lynx Software Technologies, which primarily on the market of embedded systems is aligned. Although the application areas include predominantly critical applications in military, aerospace, medical, industrial process and control systems as well as telecommunications and consumer electronics.
47. Chakra

48. Linux Lite

DSOS (Deep Six Operating System) was a real-time operating system (sometimes referred to as an operating system kernel) developed by Texas Instruments' Geophysical Services division (GSI) in the mid-1970s.
50. FuryBSD

IDE, ATAPI, soundblaster, FDC, VGA, NE2000, parallel port, serial port, RTC, keyboard, ALI1543 SMB. supported filesystems:- VFAT [FAT32/FAT16/FAT12], NTFS, ext2, CD Filesystem [ISO9660/Rock Ridge Extension/Joliet Extension], HPFS.
52. OS/2

brickOS (previously legOS) is an alternative software environment for the Lego Mindstorms Robotic Invention System. The intent is to allow developers to write C and/or C++ code for the RIS platform.
Operating System ISIS (Intel System Implementation Supervisor) was originally developed by Ken Burgett to Intel under the new management Bill Davidow from 1975 for systems Development their Microprocessor (IMDS) processors 8080/8085, and later adapted as ISIS-II for FDD systems.
55. Q4OS

56. NSK (NonStop Kernel)

In 1983, the NonStop TXP CPU was the first reimplementation of the TNS instruction set architecture. It consisted of standard TTL chips and programmable array logic chips, with 4 boards per CPU module. Cache Memory was used for the first time.
μClinux is a Linux distribution with a kernel adapted to microprocessors and microcontrollers without Memory Management Unit.
58. Xandros

59. Salgix

Salgix is GNU/Linux-based OS developed and maintained by GMSI built with Debian and Ubuntu technology specifically for use on its line of Visual Workstations.
60. Arch Linux

61. OS/9

62. NetBSD

63. Harmony

64. CentOS

65. OS/2 Warp

66. FreeDOS

67. Sinclair

68. Firefox OS

69. VMS

70. KolibriOS

71. z/OS

72. PowerOS

73. MikeOS

74. PAKOS

75. Netware

76. ScorchOS

77. UbuntuME

78. VxWorks

79. PC-MOS/386

80. Windows Vista

81. Mac OS 9

82. WinMac

83. BlueEyedOS

84. ConvexOS

85. Lycoris Desktop/LX

86. Fuchsia

87. AdaOS

88. TinyOS

89. Data General

90. Masix

91. NetMAX DeskTOP

92. Raspbian

93. Windows 11

94. Ufficio Zero

95. Windows ME

96. L4

97. BIG LINUX

98. Allegro

99. Ultrix

100. BeOS

101. MeeGo

102. DesktopBSD

103. Chimera

104. Windows XP

105. Windows Server 2003

106. Windows Server 2008

107. MidnightBSD

108. REXX/OS

109. System 6 (Mac OS)

110. Windows 2000

111. Windows CE

112. Zebuntu

113. Alpha OS

114. OS/400

115. ParallelKnoppix

116. Windows Server 2008 R2

117. MorphOS

118. Thix

119. StreamOS

120. Kylin

121. MOSIX

122. XtreemOS

123. HydrixOS

124. OppcOS

125. Windows 98

126. ITS

127. Palm OS

128. z-VM

129. RISC OS

130. osCAN

131. SLAMPP

132. FullPliant

133. LindowsOS

134. eComStation

135. Windows 95

136. Spice

137. DC/OSx

138. JAMB

139. Novell DOS

140. SymbOS

141. ThreadX

142. GUIDE

143. TriangleOS

144. HP-UX from HP

145. Zentyal

146. AIX

147. Coherent

148. PC-BSD

149. SliTaz GNU/Linux

150. ERaMS

151. Symphony OS

152. CP/M

153. OpenSolaris

154. Windows Automotive

155. DOS

156. Power Desktop

157. RTMX

158. PETROS

159. Bada

160. PublicOS

161. PC-DOS

162. A/UX

163. ProOSEK

164. OS-9

165. CP/K

166. CP/Z

167. Oasis

168. Cisco IOS

169. QNX

170. NOS/VE

171. Unix System

172. SunMOS

173. ZotOS

174. Lisa OS

175. ClearOS

176. CP/NET

177. IRIX

178. OS-2

179. OpenBeOS

180. OpenServer

181. Jbed

182. DIGITAL UNIX

183. Oaesis

184. OpenLinux

185. STAR-OS

186. IRTS

187. ModulOS

188. Amstrad

189. NeXTSTEP (foundation for OS X)

190. PSOS

191. Urli OS

192. Yggdrasil Linux

193. DELL UNIX

194. GEOS

195. THE

196. DOS2

197. Solaris from Sun Microsystems

198. OS-C

199. SCO OpenServer

200. TRS-DOS

201. BSDi

202. Beowulf

203. Chorus

204. Cinder OS

205. Darwin

206. L13Plus

207. LAN Manager

208. LDOS

209. LNX-BBC

210. MicroVMS

211. Solar_OS

212. Kaspersky OS

213. CDOS

214. CMW+ (SCO)

215. COBRA

216. CONSENSYS

217. CPF (Control Program Facility)

218. CSOC

219. CTOS

220. CTSS

221. CX/SX

222. Calmira

223. Cefarix

224. Chaos

225. ChibiOS

226. Chippewa OS

227. Clicker32

228. Contiki

229. Cosy

230. Cronus

231. Cygnus

232. DAC

233. DCP

234. DEMOS

235. DESKWORK

236. DG/UX

237. DK/DOS

238. DLD

239. DNIX

240. DOS 50

241. DR-DOS

242. DTOS

243. DVIX

244. DYNIX Unix (Sequent)

245. Degenerate OS

246. Delitalk

247. Deming OS

248. Domain OS

249. Dosket

250. Draco Linux

251. Dragon Linux

252. Drops

253. Drywell OS

254. ECL-3211

255. EGOS

256. ELKS

257. EOS

258. EP/IX

259. EPOC

260. ERIKA

261. EROS

262. ESER

263. ESIX

264. ESKO

265. EduOS

266. Elate

267. Elysium

268. EuNIX

269. Eumel

270. ExOS

271. Exopc

272. Express

273. FDOS

274. FLP-80 DOS

275. FMS

276. Famos

277. Fiasco

278. Flamethrower

279. FlashOS

280. FlexOS

281. FlingOS

282. Flux

283. Flux-Fluke-Flask

284. FoX Desktop

285. Forth

286. FortiOS

287. FreeDOWS

288. FreeVMS

289. Frenzy

290. FunatixOS

291. FxOS

292. GCOS

293. GECOS

294. GEORGE

295. GM OS

296. GNU Hurd

297. GNUstep

298. GazOS

299. GeekOS

300. Gemini Nucleus



































